Total knee replacement exercises are essential for recovery, improving mobility, and strengthening muscles. PDF guides provide structured routines, including knee flexion, extensions, and strengthening exercises to ensure proper healing and restore function.

Importance of Early Mobilization
Early mobilization after total knee replacement is crucial for a successful recovery. It helps improve blood circulation, reducing the risk of blood clots and swelling. Moving the knee early prevents stiffness and promotes healing. Regular exercise strengthens muscles around the knee, improving stability and range of motion; Early movement also prevents muscle atrophy and supports joint flexibility. Additionally, it minimizes the risk of complications like deep vein thrombosis. A structured routine ensures gradual progress, avoiding overexertion. Early mobilization sets the foundation for intermediate and advanced exercises, leading to better long-term outcomes. Consistency and adherence to prescribed exercises are key to achieving optimal results and restoring knee function.
Role of Exercise in Recovery
Exercise plays a vital role in recovery after total knee replacement, enhancing strength, flexibility, and joint stability. It helps restore normal knee function, enabling patients to return to daily activities and improve overall quality of life. Regular exercises promote muscle balance, reducing the risk of future injuries or complications. Strengthening the surrounding muscles, such as quadriceps and hamstrings, provides essential support to the new knee joint. Additionally, exercises improve circulation, which aids in healing and reduces swelling. Consistency in following a structured exercise routine ensures gradual progress and prevents setbacks. Over time, exercise helps patients regain confidence and independence, making it a cornerstone of the recovery process. By adhering to prescribed exercises, individuals can achieve optimal outcomes and maximize the benefits of their total knee replacement.

Immediate Post-Surgery Exercises
Immediate post-surgery exercises focus on restoring knee mobility and strength. Techniques like knee flexion, extension, and straight leg raises are essential to prevent stiffness and promote circulation in the early recovery phase.
Knee Flexion and Extension
Knee flexion and extension exercises are foundational for restoring mobility after total knee replacement. These movements involve bending and straightening the knee to improve range of motion and reduce stiffness. Patients are encouraged to perform these exercises gently, often with the aid of a towel or pillow for support.
Start by sitting or lying down with the leg extended. Slowly bend the knee as far as comfort allows, then straighten it again. Repeat this 10-15 times, 2-3 times daily. Progress gradually to achieve full extension and flexion. Consistency is key to avoiding stiffness and promoting circulation. These exercises are typically performed in the immediate post-surgery phase to lay the groundwork for more advanced movements later in recovery. Patience and adherence to a daily routine are essential for optimal outcomes.
Straight Leg Raises
Straight leg raises are a simple yet effective exercise to strengthen the muscles around the knee after total knee replacement. To perform this exercise, lie on your back with the unaffected leg bent and the affected leg straight. Tighten the muscles on the top of your thigh by pressing the back of your knee into the floor. Slowly lift the straight leg to the height of the bent knee, keeping it straight throughout the movement. Hold for a few seconds, then lower it slowly. This exercise helps improve circulation, strengthens the quadriceps, and promotes proper healing. It is essential to maintain control and avoid bending the knee during the lift. Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions daily, as outlined in most total knee replacement exercise PDF guides. This exercise is typically introduced in the immediate post-surgery phase to build a foundation for more advanced movements later in recovery.
Ankle Pumps
Ankle pumps are one of the first exercises recommended after total knee replacement surgery. They are simple to perform and help improve circulation, reduce swelling, and prevent blood clots. To do an ankle pump, lie on your back or sit in a chair with your leg straight. Flex your foot up toward your head, then point it down away from you. Repeat this movement slowly and smoothly, continuing for 10-15 repetitions. Perform this exercise every 1-2 hours, especially in the early stages of recovery, to promote healing and maintain mobility. Ankle pumps are a foundational exercise that can be done anywhere and are often included in total knee replacement exercise PDF guides as part of the immediate post-surgery routine; Consistency is key to achieving the best results and ensuring a smooth recovery process.

Intermediate Phase Exercises
Intermediate exercises focus on strengthening and improving mobility. Heel slides, step-ups, and wall-assisted exercises are common, helping restore knee function and prepare for daily activities. Consistency is crucial for progress.
Heel Slides
Heel slides are a foundational intermediate exercise for total knee replacement recovery. Start by lying on your back with your affected leg straight and the other knee bent for support. Slowly slide the heel of your affected leg toward your buttocks, bending your knee as far as comfort allows. Hold for 5 seconds, then gradually slide your leg back to the starting position. Perform 3 sets of 10 repetitions daily. This exercise improves knee flexion, reduces stiffness, and strengthens surrounding muscles. Breathing deeply during the movement can help relax the leg. Avoid forcing the knee beyond a painful range, as this may hinder progress. Consistency is key to gradually increasing mobility and strength. Over time, as comfort improves, the exercise can be done while sitting or standing to further challenge the knee joint.
Step-Ups
Step-ups are an effective intermediate exercise for improving strength, balance, and mobility after total knee replacement. To perform a step-up, stand in front of a sturdy, low step or platform (4-6 inches high). Place the foot of your affected leg on the step, keeping your knee straight. Slowly transfer your weight onto the affected leg, bending the knee to step up while bringing the other foot onto the platform. Hold for 2-3 seconds, then step down with the same leg, returning to the starting position. Perform 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each leg. As strength improves, the step height can gradually increase; This exercise targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles, enhancing functional mobility. Proper form is crucial to avoid strain, so consider using a handrail for support if needed. Consistency with step-ups will help restore confidence in daily activities like climbing stairs or walking uneven terrain.
Wall-Assisted Exercises
Wall-assisted exercises are a valuable component of the intermediate phase of total knee replacement rehabilitation. These exercises utilize a wall for support, reducing strain on the knee while promoting strength and flexibility. One common exercise is the wall slide: stand with your back against the wall and feet about 12 inches away. Slowly slide down the wall, bending your knees to a 45-degree angle, and hold for 10 seconds before returning to the starting position. Another effective exercise is wall-assisted mini squats, where you use the wall to stabilize yourself while performing partial squats. These exercises improve range of motion, strengthen the quadriceps, and enhance overall knee stability. They are particularly beneficial for patients who may struggle with balance or weight-bearing activities. Consistency with wall-assisted exercises can significantly accelerate recovery and prepare the knee for more advanced movements.
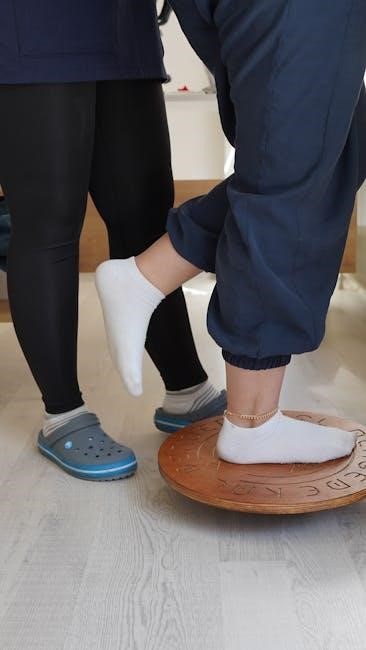
Advanced Phase Exercises
Advanced phase exercises focus on improving balance, strength, and functional mobility. Activities include agility drills, balance exercises, and resistance training to enhance knee stability and restore normal function.
Balance Exercises
Balance exercises are crucial in the advanced phase of recovery after total knee replacement. These exercises help improve stability, coordination, and overall functional mobility; Common balance exercises include standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, and using a wobble board. Patients are often advised to perform these exercises near a stable object, such as a chair or wall, for safety. As balance improves, the support can gradually be removed. Additionally, exercises like single-leg squats and balance reaches are incorporated to challenge the patient further. These activities not only enhance knee stability but also reduce the risk of falls. Consistency is key, and patients should aim to practice these exercises daily as part of their routine. Over time, improved balance contributes significantly to the patient’s ability to perform daily activities with confidence and independence.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are a critical component of the advanced phase of recovery after total knee replacement. These exercises aim to restore muscle strength, particularly in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, which are essential for knee stability and function. Common strengthening exercises include straight leg raises, mini squats, and step-ups. Patients are often advised to use resistance bands or light weights to gradually increase muscle strength. Progression to more dynamic exercises, such as leg presses and balance exercises, helps improve overall knee function. Strengthening exercises not only enhance mobility but also reduce the risk of future injuries. Consistency is key, as regular practice ensures continued improvement in muscle strength and joint stability. Over time, these exercises enable patients to resume daily activities and even participate in low-impact sports with confidence.

Common Complications and How to Avoid Them
Common complications after total knee replacement include blood clots, infections, and knee stiffness. To avoid these, adhere to prescribed exercises, follow medical advice, and maintain proper wound care.
Overexertion
Overexertion is a common risk during the recovery phase of total knee replacement. It occurs when patients push their knee beyond its current capacity, leading to pain, swelling, or even setbacks in recovery. Early mobilization is crucial, but it must be balanced with rest to allow proper healing. Performing too many exercises or using excessive force can strain the knee joint and surrounding muscles, potentially causing damage to the new prosthetic or soft tissues. To avoid overexertion, patients should strictly follow the exercise routines prescribed by their physical therapist and avoid activities that cause significant pain or discomfort. It’s important to listen to your body and gradually increase activity levels to ensure a safe and effective recovery. Overexertion can delay progress, so consistency and moderation are key.
Poor Form
Poor form during total knee replacement exercises can hinder recovery and lead to ineffective or even harmful outcomes. Proper technique ensures that muscles and joints are engaged correctly, promoting healing and strength. Incorrect form may result in muscle imbalances, strain on the prosthetic, or prolonged recovery. Patients should focus on maintaining proper alignment, avoiding compensatory movements, and using controlled, slow motions. For example, during straight leg raises, the leg should remain straight, and the core should be engaged to prevent hip or lower back strain. Using mirrors or recording exercises can help patients monitor their form. Starting with shorter sessions and gradually increasing duration can also prevent fatigue, which often leads to poor form. Consistency and attention to detail are critical to achieving optimal results and avoiding complications. Always consult a physical therapist if unsure about proper technique to ensure exercises are performed safely and effectively.

Importance of Consistency
Consistency in performing total knee replacement exercises is crucial for optimal recovery. Regular practice helps strengthen muscles, improve joint stability, and restore mobility, ensuring long-term success and minimizing setbacks.

Creating a Daily Routine
A daily routine is vital for successful recovery after total knee replacement. Start with gentle exercises like ankle pumps and knee flexions, gradually incorporating intermediate and advanced movements. Consistency ensures proper healing, strengthens muscles, and restores mobility. Allocate specific times for exercises, such as morning and evening sessions, to maintain discipline. Use a structured plan from PDF guides to track progress and stay motivated. Incorporate rest periods to avoid overexertion, as recovery is as important as exercise. Over time, increase intensity and duration to achieve long-term benefits. A well-organized daily routine helps patients regain independence and return to normal activities efficiently. Stick to the routine consistently to maximize recovery outcomes and avoid setbacks. Proper time management and adherence to the plan are key to achieving optimal results. PDF guides provide comprehensive routines tailored to each recovery phase, ensuring a smooth transition from post-surgery to full mobility.
Tracking Progress
Tracking progress is crucial for a successful recovery after total knee replacement. Use a journal or PDF guide to monitor improvements in flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Record daily achievements, such as increased knee flexion or reduced pain levels, to stay motivated. Many PDF guides include checklists or progress logs to help patients visualize their advancements. Regularly assessing progress helps identify areas needing improvement and ensures exercises are performed correctly. Share updates with your physical therapist to adjust routines as needed. Celebrate small milestones, like walking without assistance or climbing stairs, to maintain enthusiasm. Consistent tracking also helps prevent plateaus and keeps patients accountable. Over time, seeing measurable progress reinforces the importance of adhering to the exercise plan. PDF guides often provide clear benchmarks to measure success, ensuring patients stay on track throughout their recovery journey.

Resources for Total Knee Replacement Exercises
Access comprehensive PDF guides on total knee replacement exercises, offering detailed routines, recovery tips, and progress trackers. These resources are often available on hospital websites or orthopedic clinics, ensuring patients have structured plans for optimal recovery.
PDF Guides
PDF guides are an excellent resource for patients undergoing total knee replacement, offering comprehensive exercise routines and recovery tips. These guides often include detailed illustrations and step-by-step instructions for exercises like knee flexion, extensions, and strengthening movements. Many PDFs are designed by orthopedic specialists and physical therapists, ensuring the information is both safe and effective. They also provide tips on creating a daily routine, tracking progress, and avoiding common complications. PDF guides are easily accessible online, often available for free from hospital websites or orthopedic clinics. Patients can download them and refer to them anytime, making them a convenient tool for home rehabilitation. These guides emphasize the importance of consistency and proper form, helping patients achieve the best possible outcomes after surgery.
- Include detailed exercise routines and recovery tips.
- Offer step-by-step instructions for proper form.
- Provide tracking tools for monitoring progress.
- Are accessible online for easy reference.
Online Tutorials
Online tutorials are a valuable resource for patients recovering from total knee replacement surgery. These tutorials often include video demonstrations of exercises, such as knee flexion, extensions, and strengthening routines. Many are hosted on platforms like YouTube or hospital websites, providing accessible guidance for patients to follow at home. Video tutorials are particularly helpful because they show proper form and technique, reducing the risk of injury or poor form. Some online resources also offer structured programs tailored to different phases of recovery, from immediate post-surgery to advanced strengthening. Patients can track their progress and adjust their routines based on the tutorials. Additionally, interactive tools and forums may accompany these tutorials, allowing patients to ask questions or share experiences. Overall, online tutorials enhance the recovery process by offering visual and practical guidance, ensuring patients stay on track with their exercise routines.
- Video demonstrations for proper form and technique.
- Structured programs for different recovery phases.
- Interactive tools for tracking progress.
- Accessible on platforms like YouTube or hospital websites.

0 Comments